All spiders are believed to be venomous, most lack the strength of tentacles to pierce the skin and inject venom.
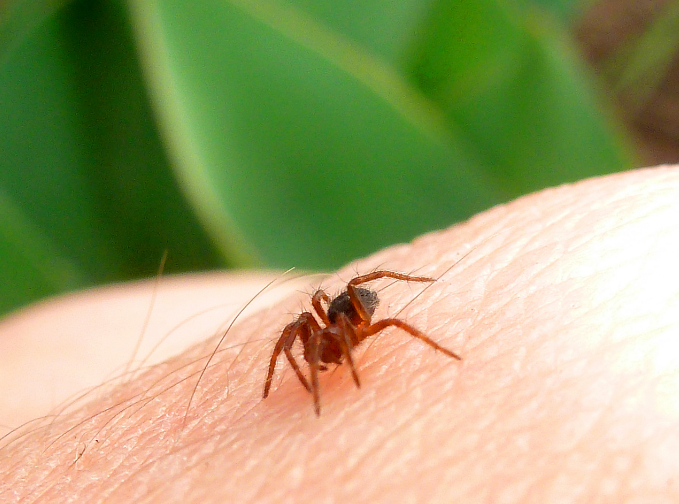
Spiders are not aggressive animals and the bites are actually accidental, and they occur during gardening, camping, sitting in the grass, working with hay and vines, sitting in abandoned buildings and the like.
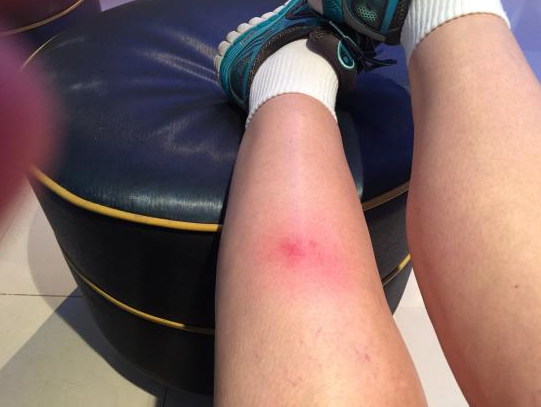
What does a spider bite look like?
The spider bite is frequently undetectable or causes very minor discomfort. Because most spiders do not have powerful enough tentacles to pierce the skin, but they are considered to be almost all venomous.
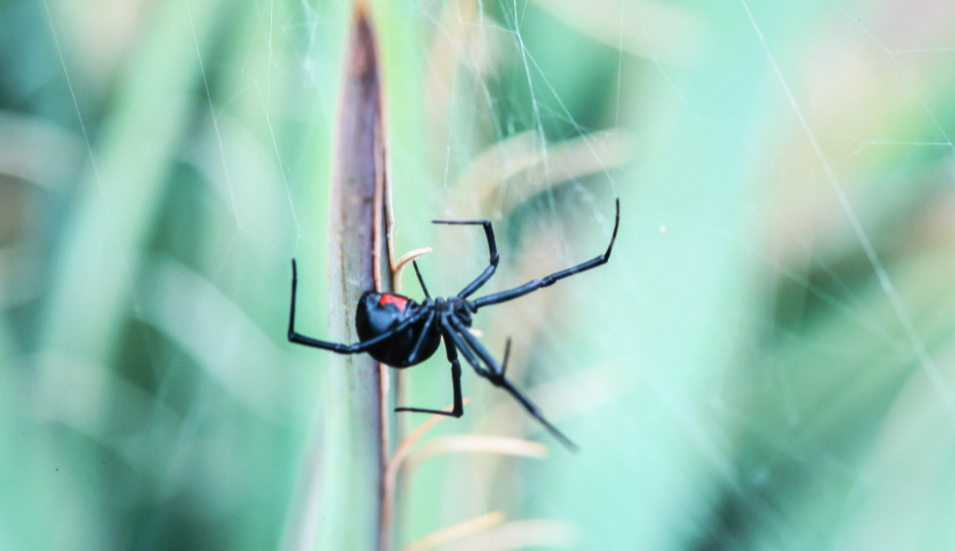
Spider venom poisoning is called arachnidism, araneism, or araneism. Latrodism is the most important part of araneism and is a series of symptoms caused by the action of the venom of the spider Latrodectus tredecimguttatus, (black widow). The venom apparatus of latrodux consists of hollow clamps, venom glands, and their excretory ducts.
Find out more about: These Healthy Foods Can Be Dangerous If You Consume Them In Large Quantities
What happens in the body when the (dangerous) spider bites you
The spider pierces the skin with its tentacles and injects venom from within the gland into the victim’s (human) body. The neurotrophic toxin, which is made up of toxalbumin and phospholipid lipoproteins, affects both centrally and peripherally on the autonomic and central nervous systems.
Appearance of the first symptoms
From the time the sting occurs to the onset of the first symptoms, it takes from ten minutes to an hour. The discomfort starts in the localised lymph nodes and then extends throughout the body. The patient complains of chest tightness and pressure, as well as sweaty skin and muscle spasms. The agony eventually fades, leaving a burning sensation in the feet. The patient normally feels considerably better on the third day, although he still has leg discomfort and burning in his feet, as well as tingling and a headache. Some patients may develop a skin rash after a few days.
Symptoms last an average of seven days in untreated patients, although they can linger as long as three weeks in extreme cases. Although catastrophic outcomes are uncommon, certain patients, particularly those with heart disease or high blood pressure, may experience complications that are lethal. Lethargy is treated with symptomatic (muscle relaxants, analgesics, and calcium) and targeted (antitoxin) therapy. A doctor should always be consulted following a black widow ode.
After a spider bite, it is always necessary to wash, disinfect and apply a cold compress to the skin at the site of the sting. It is required to apply corticosteroid cream in the case of redness and swelling, and antibiotic cream prescribed by a doctor in the case of infection and pus.
In children, a pediatrician examination is always necessary, and in adults a professional examination is necessary in case of a black widow sting or in case of a stronger local skin reaction to the bite of another spider, in case of a systemic reaction or rash.