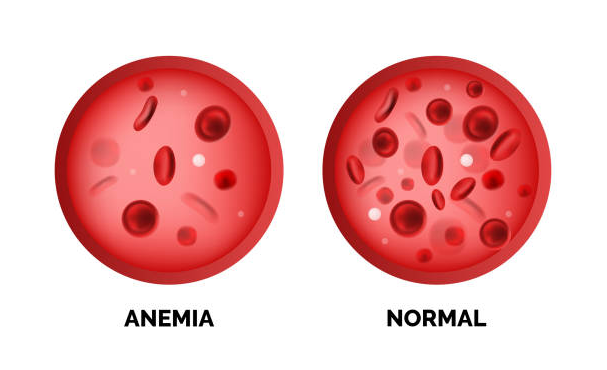
Anemia is a condition in which the number of red blood cells, or the concentration of hemoglobin, is reduced to zero. Hemoglobin shortage creates health difficulties because it permits oxygen to be transported to all tissues in the body. Normal functioning is impossible without oxygen.
Anemia comes in many forms, with iron deficiency anemia being one of the most frequent.
What represents?
Iron deficiency anemia, also known as sideropenic anemia, is characterized by a shortage of healthy red blood cells in the blood, which provide the body with energy and a youthful appearance.
Because the body cannot manufacture hemoglobin without iron, this type of anemia arises when the body does not have enough of it. In this instance, oxygen is not transported evenly throughout the body, resulting in weariness, exhaustion, weakness, and pale complexion.
Iron deficiency anemia is far more common in women, particularly those of reproductive age, hence iron intake should be monitored more closely.
Symptoms
Anemia develops gradually, so it is very difficult to notice the symptoms at first. Over time, the anemia worsens and the symptoms become more noticeable. Some of the symptoms by which you can recognize the presence of anemia are:
- fatigue, exhaustion
- dizziness
- headaches
- very pale complexion
- problems with concentration
- brittle nails
- shortness of breath
- cold feet and palms
- irregular heart rhythm
- absence of appetite
- restless legs syndrome
- unusual need to consume ice
If you suspect you have anemia, see a doctor. With the help of blood tests and physical examination, anemia can be diagnosed and treatment can be started immediately.
Reason for the occurrence
If you do not consume enough iron or for some reason you lose a lot of iron, then the body can not produce enough hemoglobin and anemia occurs. The most common causes of this type of anemia are:
- Inadequate iron intake in the body. Many people are concerned about having adequate vitamins but overlook the need of critical minerals. Sufficient iron intake is required for normal body functioning and the prevention of anemia, particularly through nutrition.
- There is a loss of blood. Because red blood cells contain iron, if you lose blood, you also lose iron. Blood loss and anemia can be caused by heavy menstruation or abdominal bleeding.
- Inability of the body to absorb iron. Dietary iron is absorbed through the initial part of the small intestine. Various diseases of this part of the intestine or surgical removal of part of the intestine can disrupt the normal absorption of iron.
Risk groups
- This kind of anemia is more common in women of childbearing age, owing to blood loss during menstruation. Women with thick periods and pregnant women should take extra precautions.
- Children and newborns. Anemia is more likely in newborns who are born underweight or prematurely. Iron deficiency anemia is more likely to occur in children who do not eat a balanced and diverse diet.
- Meat contains a lot of iron. Vegetarians are more likely to acquire anemia because they don’t eat meat. Furthermore, iron from animal products (red meat, liver, and eggs) is more easily absorbed by the body than iron from plant-based diets.
- People who suffer from stomach disorders. Because this group’s iron absorption is slower, individuals have a difficult time meeting their daily iron requirements.
Treatment
If your doctor concludes that you have iron deficiency anemia, iron tablets will almost certainly be prescribed. The majority of patients feel better within just one week, however treatment normally lasts several months.
Do not start anemia treatment on your own if you suspect you have it.
Prevention
If you eat enough iron-rich foods like hog liver, cow kidneys, red meat, fish, flour, almonds, beans, and egg yolk, you can easily avoid iron deficiency anemia. Spinach, buckwheat, strawberries, kiwifruit, cauliflower, broccoli, potatoes, and tomatoes are all high in iron.
When consuming iron-rich foods, avoid tea, coffee, milk and soy, as they prevent the absorption of iron. Calcium also prevents absorption. Therefore, if you take extra minerals out of the diet, avoid the iron-calcium combination.
Whenever you eat foods rich in iron, to improve absorption, eat foods rich in vitamin C, such as citrus juices (orange, grapefruit), fruits (strawberries, apricots, kiwi) or vegetables (broccoli, tomatoes).