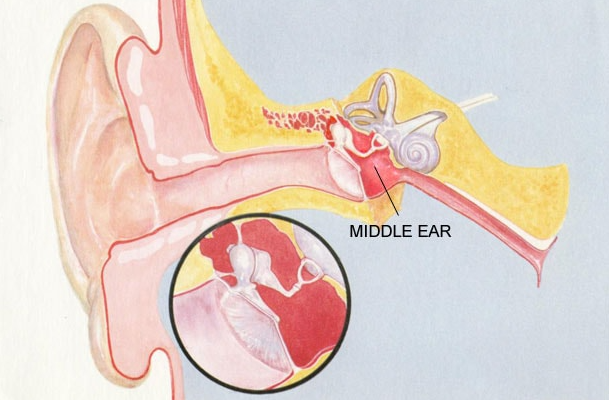
Adults and toddlers alike suffer from ear pain. One of the most popular reasons for parents to take their children to the doctor is for this reason. Otalgia can affect one or both ears, have a variety of characteristics (sharp, dull, scorching pain), and be of varying intensity (from mild to unbearably strong pain).
REASONS FOR OTHALGY
Otalgia is mainly caused by an ear injury, infection, or irritation, although it can also be caused by radial discomfort in some circumstances. Radial pain is caused by an injury or infection to structures surrounding the ear, such as the teeth or jaw, and extends to the ear, simulating otalgia.
The most common causes of otalgia:
- Acute or chronic otitis (inflammation of the ear);
- Ear injuries due to pressure changes;
- Presence of cerumen (earwax);
- Foreign body in the ear;
- Inflammation of the throat;
- Sinusitis;
- Shampoo or water in the ear.
Rare causes of otalgia:
- Eardrum perforation;
- Temporomandibular joint syndrome;
- Arthritis affecting the temporomandibular joint;
- Tooth infection;
- Tooth injury;
- Ear canal eczema;
- Trigeminal neuralgia.
HOW TO HELP YOURSELF AT HOME?
There are several ways to reduce ear pain at home. The most commonly used are:
- Applying a cold compress on the eardrum for a period of 15-20 minutes;
- Protection of the ear from water ingress;
- Using ear drops (this procedure does not apply if there is a rupture of the eardrum);
- Taking painkillers;
- Chewing gum relieves pressure, and thus the pain caused by an ear infection;
- An upright, upright body position can reduce pressure in the middle ear.
WHEN SHOULD YOU VISIT A DOCTOR?
It is necessary to consult your doctor if:
- Body temperature is above 38 ° C;
- New symptoms such as dizziness, headache, swelling around the ear, weakness of the facial muscles;
- There is a sudden cessation of previously strong otalgia, which usually alludes to perforation of the eardrum;
- Blood or pus leaks from the ear;
- Symptoms such as pain, fever, chills or irritability do not improve within 24-48 hours.