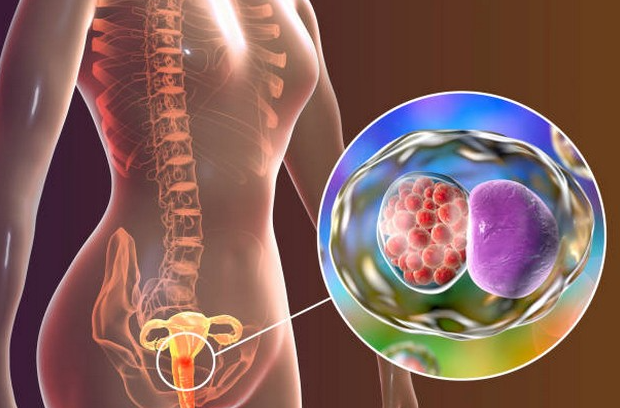
Chlamydia is known as the “silent killer,” and there’s a reason for that: a new study has revealed why the disease is so hazardous.
According to a recent report by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, one out of every 100 people in the United States has a sexually transmitted disease. In other words, chlamydia affects nearly 1.8 million people in the United States.
Even more concerning is the fact that up to 400,000 infected people are likely ignorant that they have the disease and are consequently passing it to their partners.
It is important to note that those infected are not to blame for the spread of the disease, as chlamydia does not have any symptoms that will make you get tested.
“Chlamydia can, but does not have to, cause fatigue and pain in both sexes, particularly when urinating. “However, it’s difficult to predict how it will develop in each individual because no symptom is solely chlamydial, nor is it a sure sign that you have the disease,” said Yale professor Mary Jane Minkin.
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections, with women being far more likely to contract it.
The disease is spread by sex in the vaginal, anal, and oral areas. If the germs get into touch with the eyes, a person can become infected with chlamydia. This is quite unusual.
Chlamydia is not spread through normal contact, therefore you can’t get it through sharing beverages or food, kissing, holding hands, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or going to the bathroom.
The easiest way to avoid infection is to use condoms.
If left untreated, the condition can lead to infections of the urethra, vaginal canal, and cervix. At the same time, chlamydia can damage both men and women’s fertility.
Chlamydia can also cause internal genital irritation, which is quite painful.
Fortunately, your doctor can do a test to see if you have the disease. Once detected, chlamydia is treated with antibiotics.