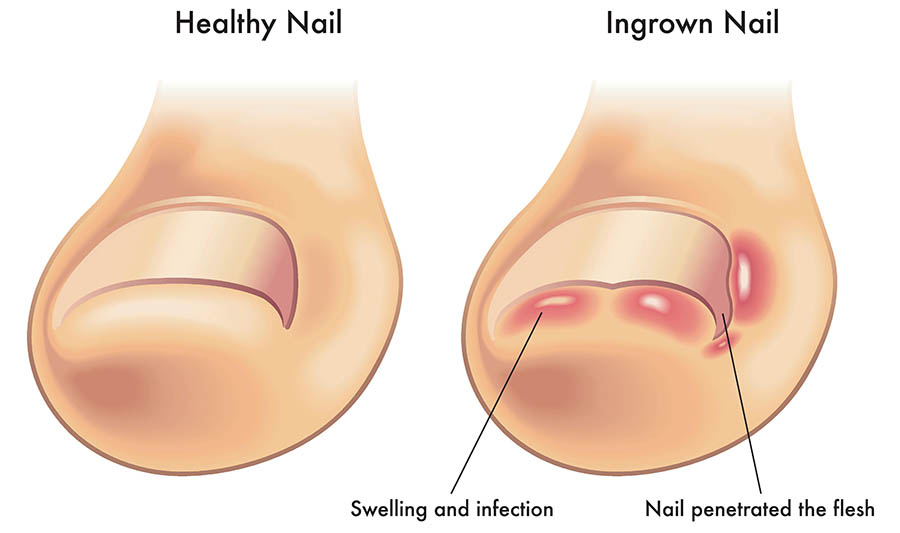
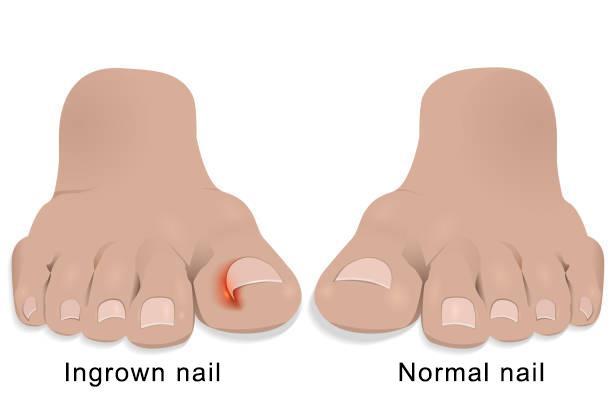
When a nail begins to grow curled into the skin, it results in ingrown toenails, which are extremely painful and uncomfortable. As a result, it causes an infection as well as swelling, discomfort, irritations, and redness.
Ingrown toenails are primarily brought on by genetics, unsuitable footwear, and foot injuries. This problem is fairly widespread and frequently too challenging to address.
However, there are a number of efficient natural treatments to relieve the resulting pain. Keep in mind not to cut or clip the nail, and it is always preferable to speak with your doctor before trying anything new.
You will quickly experience tremendous relief using the next five ways, which are all very effective:
Floss or a Cotton Ball
To release the tension between the painful toe and the nail, use a cotton ball or some flow. To carefully lay a sterile cotton ball underneath the nail and make sure it is at a comfortable height above it, carefully lift the nail with tweezers (or dental floss wrapped around the nail).
Find out more about: Here is How To Instantly Stop A Migraine With Salt
Epsom salt added to a warm bath
Epsom salts soften nails, soothe irritated skin, and clean the foot of bacteria. Simply leave the foot in the lukewarm salt water for 20 minutes.
Tea Tree Oil
This oil works well as a natural cleaner. Applying a few drops of it to the afflicted area is all that is necessary
Antibiotic Ointment
Given the vulnerability and core location of the affected area, it is crucial to keep the feet clean. Since the feet come into contact with so many bacteria, you should frequently apply antibiotic ointment and wrap the toe in a bandage to keep it sterile.
Apple Cider Vinegar Wash
When treating an ingrown toenail, vinegar works well. To ease the pain and suffering, you should just dilute a quarter cup of it in some warm water and bathe your feet in it.
Additionally, if you apply it directly to the wound, its strong antibacterial characteristics will clean the area and help prevent infection. However, it is unable to combat an ongoing bacterial infection.