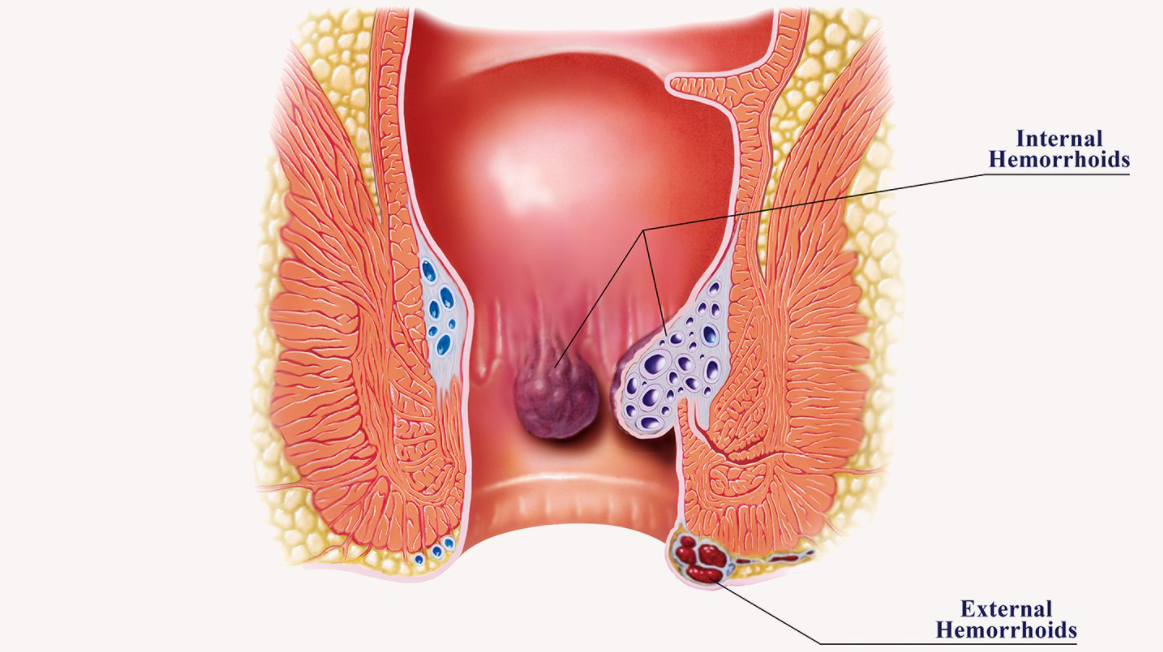
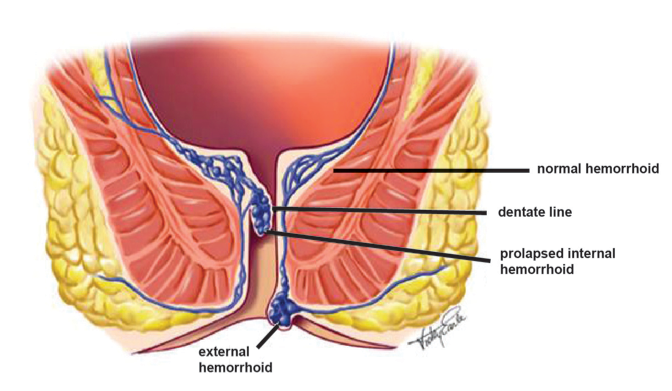
Hemorrhoids are a part of the anal canal’s vascular system, which has the primary role of controlling bowel motions. The anal pads become dysfunctional and hemorrhoidal illness develops when they become irritated and swollen.
By the age of 50, it is anticipated that more than half of the population will be suffering from hemorrhoids. Both men and women are affected by the disease.
Severe itching, tingling, discomfort, and bleeding in the anal area are all signs of inflammation and should not be disregarded.
They are diagnosed by a specialized medical expert performing a physical rectal examination, and depending on the issue, you may be asked to undergo anoscopy or rectoscopy, which is an inspection of the last part of the digestive system, the anus and rectum.
Internal and external hemorrhoids are distinguished. External hemorrhoids are characterized by swelling, intense and severe pain, a hard lump in the anus, bleeding, and itching. Internal hemorrhoids, on the other hand, are not seen or felt and normally do not cause discomfort.
Causes of hemorrhoids:
- Constipation with hard and dry stools or diarrhea
- Strong strain during bowel movements
- Pregnancy
- Obesity
- Age, which causes tissue weakness
- Tumor of the abdominal cavity
- Too much time spent in a sitting position
- Improper diet with a small amount of fiber or very spicy and spicy foods
- Anal sex
How are hemorrhoids treated?
After most cases, the pain goes away in a week to ten days. You can use lotions, ointments, or suppositories for hemorrhoids at home, and instead of dry toilet paper, use moist and neutral (non-perfumed) toilet paper.
Sitting for lengthy periods of time should be avoided, as should lifting heavy objects. Do not put any further tension on the hoses when draining them. It’s especially crucial to make dietary modifications, such as eating more fiber-rich foods and drinking enough of water.
If the pain persists and the symptoms do not improve after a few days, see a doctor.