There are various reasons why some people are more prone to the risk of stroke.
The brain is supplied with pure blood and nutrients via big arteries. The middle cerebral artery is the largest of them all. It feeds blood to the temporal, frontal, and parietal regions of the brain’s lateral parts. The functions of the face, arms, throat, and palms are all controlled by these areas of the brain.
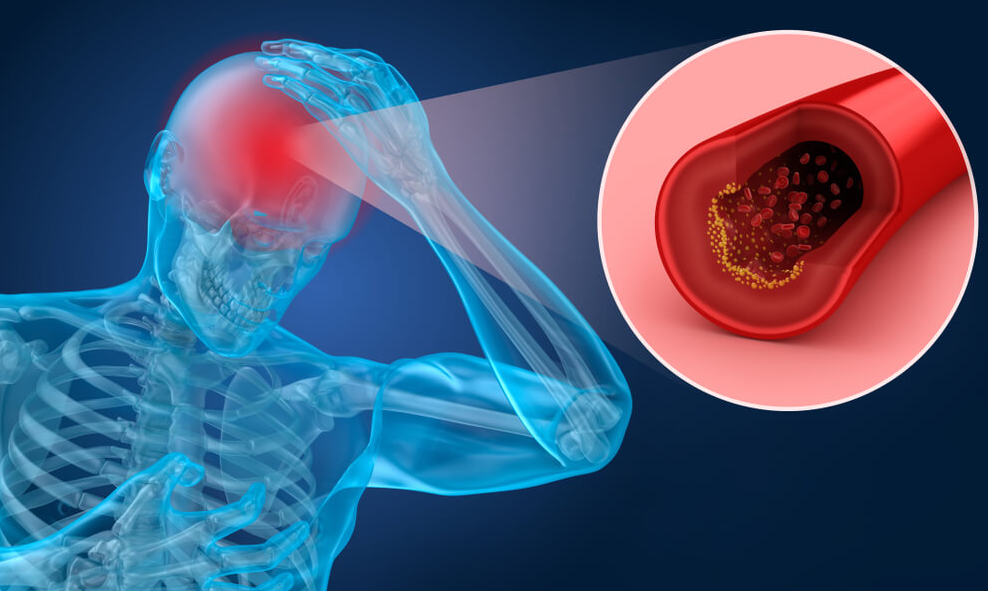
The junction of this big artery with the internal carotid arteries is frequently blocked, which can result in a stroke. When an artery or one of its branches becomes blocked, blood cannot flow adequately through it, a stroke ensues. Non-life-sustaining substances, such as blood, nutrients, and oxygen, are unable to reach the brain when such routes are closed. Permanent damage can ensue if this blockage is not removed immediately.
There are various factors that might cause a stroke in this manner, but the most prevalent are smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, and atrial arrhythmia.
A blood clot moves under pressure from an artery or the heart and lodges in the middle cerebral artery, causing a stroke. Blood clots can form directly in the artery, however this is uncommon. In either situation, a stroke through the middle cerebral artery occurs.